Galvanic zinc plating: the mysterious process that can save your metal from corrosion. Want to learn the secrets behind its operation? Read on!
Galvanic zinc plating is a process that plays a key role in protecting metals against corrosion and in the production of many everyday items. In this article, we'll explore this fascinating process, explaining what galvanizing is and how it works. Learn why it's so important and what its applications are.
What is galvanic zinc plating?
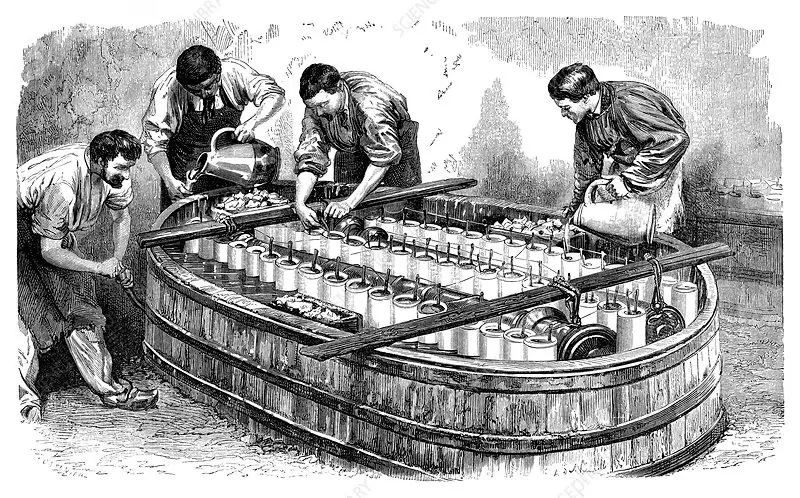
Galvanizing, also known as zinc electroplating, is an electrochemical method of coating metal objects with a layer of zinc. The process involves immersing the metal object in a solution containing zinc salts and passing an electric current through it. Through an electrochemical reaction, the zinc coats the base metal, creating a protective layer.
How does the zinc electroplating process work? The zinc electroplating process is based on electrochemistry and utilizes the principles of electric current flowing through an electrolyte. Here are the steps involved:

1. Preparing the metal object: The first step is to thoroughly prepare the surface of the metal object. All dirt, grease and rust are removed to allow for even zinc coating.
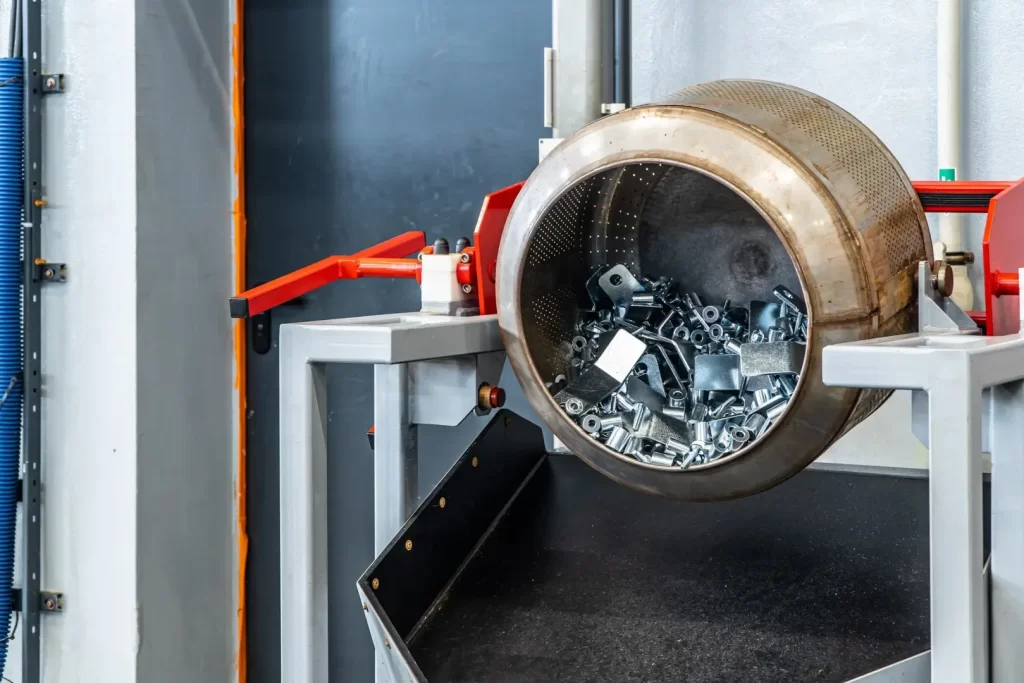
2. Immersion in solution: The metal object is then immersed in a solution containing zinc salts. This solution acts as an electrolyte that allows electric current to flow through the object.
3. Conducting Current: The metal object acts as the cathode in the electrochemical system. Current is introduced into the object, causing a redox reaction in which zinc from the solution is reduced and deposited on the surface of the object in the form of a zinc layer.
4. Formation of a zinc layer: Zinc is deposited on the surface of a metal object, creating a durable and protective layer. This layer prevents corrosion of the base metal, protecting it from atmospheric agents and moisture.
5. Finishing and Protection: Once the galvanizing process is complete, the metal object may be further finished, for example through chrome plating or painting. These additional steps provide an aesthetic appearance and additional protection against corrosion.
Applications of electroplating:
The galvanizing process has wide applications in many fields. Here are some examples:
1. Corrosion protection: Galvanic zinc plating is commonly used to protect metal surfaces, e.g. saw blades
2. Electronic Component Manufacturing: Many electronic components are electroplated to ensure durability and protection against moisture.
3. Automotive Industry: Galvanic zinc plating is widely used in the automotive industry to protect vehicle components against rust and corrosion.
4. Metal Products: Everyday products such as screws, nuts, locks and springs are often electro-galvanized to increase their durability.

Summary:
Galvanizing is an electrochemical process in which a metal object is coated with a layer of zinc to protect it from corrosion. This process is widely used in industry to produce durable and weather-resistant items. galvanic zinc plating the life of many metal structures and products can be extended.