Did you know that there's more than one galvanizing method, and choosing between them can make a huge difference in the durability and appearance of your metal product? In our latest article, we'll explore the two main techniques: hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing. Learn which method is best for your project and why the differences between them are so significant. Read on!
Hot-dip galvanizing vs. electro-galvanizing: Which method to choose?
Galvanizing is an extremely important process in the metal industry., designed to provide durability and corrosion protection to metal products. There are several different galvanizing methods, but today we'll focus on the main two: hot-dip galvanizing and electrogalvanizing. Both techniques have their advantages and disadvantages, which are worth considering before deciding which one is best for you.
Hot-dip galvanizing
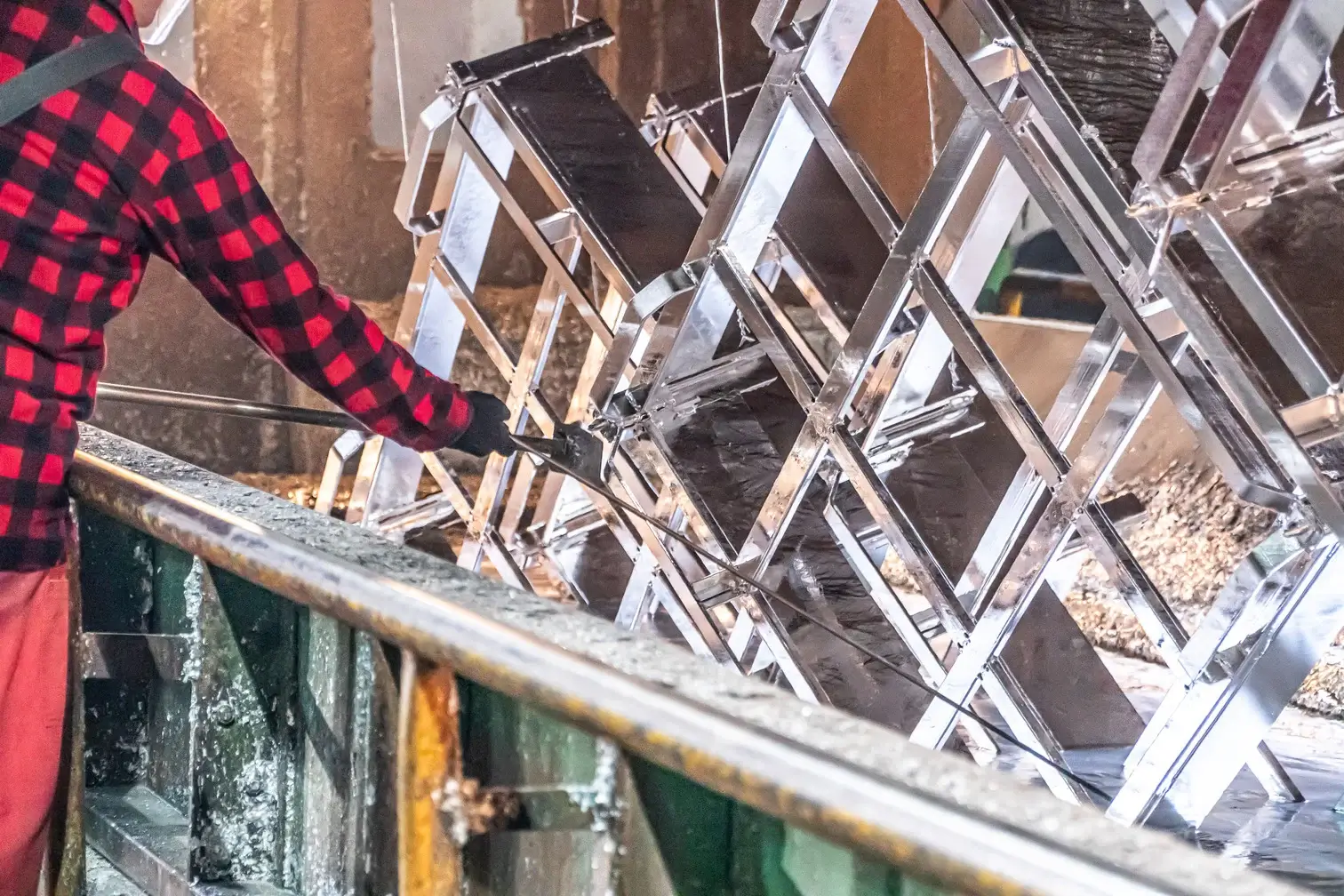
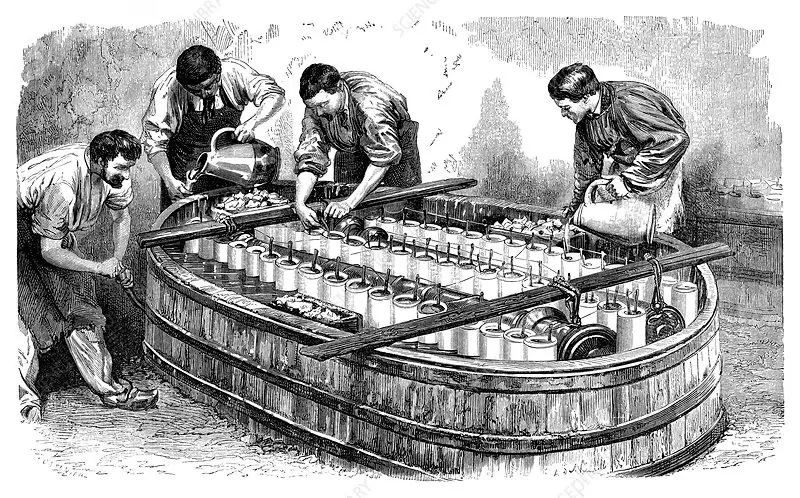
Hot-dip galvanizing This process involves immersing the prepared component in heated zinc at a temperature of approximately 450-500 degrees Celsius. This process creates a thick layer of zinc both on the outside and inside of the product. The thickness of the zinc plating using this method can range from 40 to 110 microns, making it extremely resistant to corrosion.

Advantages of hot-dip galvanizing:
- High mechanical durability: The zinc coating is thick and strongly adheres to the surface of the material, which makes it resistant to mechanical damage.
- Resistance to weather conditions: Hot-dip galvanizing offers excellent protection against weathering, making it an ideal choice for components exposed to harsh conditions.
Disadvantages of hot dip galvanizing:
- Less aesthetics: The zinc coating resulting from this process may have irregularities and streaks, which makes it less aesthetically pleasing.
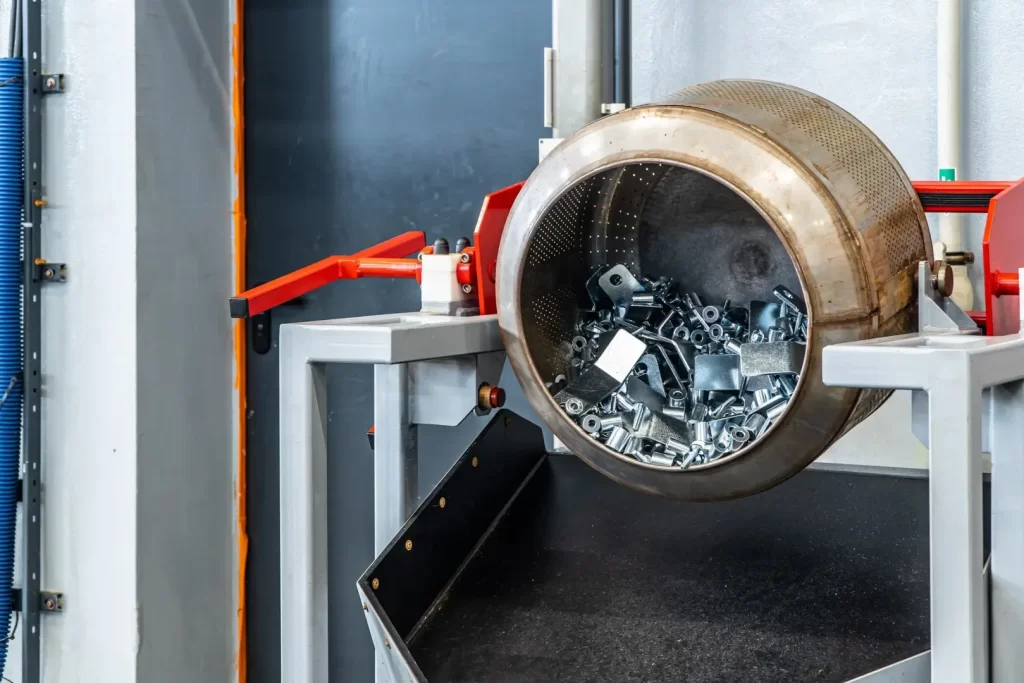
Galvanic zinc plating, also known as electroplating, is a process in which a component is immersed in an electrolyte bath, and then a thin layer of zinc is applied to the material's surface using an electric current. This method produces a smooth, imperfect zinc coating, making it visually appealing.

Advantages of galvanizing:
- Aesthetic coating: Galvanic zinc plating creates a smooth and aesthetic coating, which is why it is often used in products that are intended to be visible and decorative.
- Perfect for indoor use: This method is ideal for interior design elements and car details.
Disadvantages of electroplating:
- Lower mechanical durability: The zinc coating is thinner and less resistant to mechanical damage.
- Less corrosion resistance: Electrogalvanizing is not as corrosion resistant as hot-dip galvanizing and therefore may not be suitable for harsh weather conditions.
Choosing the right galvanizing method
The ultimate choice between hot-dip galvanizing and electro-galvanizing depends on your specific needs and applications. If mechanical durability and corrosion protection are important, especially in harsh environments, hot-dip galvanizing may be the best choice. However, if aesthetics are a priority and you want to protect internal components, electro-galvanizing may be more appropriate.
It's also worth considering costs and the end result we want to achieve. Ultimately, the choice depends on our individual needs and preferences, but now that we have full knowledge on the subject, we can make a more informed decision.